Recent Trends in European Medical Education: Digital Learning, Simulation, and the Rise of AI
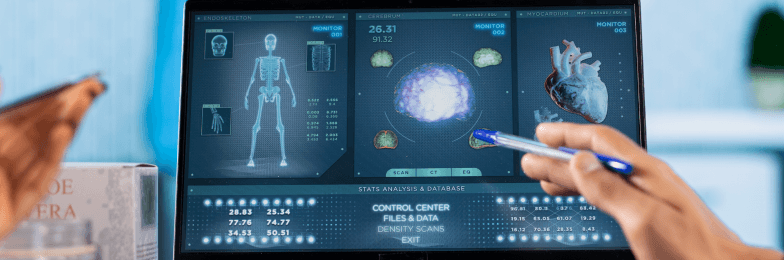
Table of Contents
- 1. Digital Learning and Online Platforms
- 2. Simulation-Based Learning
- 3. Remote Labs and Virtual Anatomy
- 4. Integration of Artificial Intelligence
- 5. Emphasis on Interdisciplinary and Global Skills
- 6. The Future of Medical Education in Europe
- Final Thoughts
Medical education in Europe is evolving rapidly. Traditional lecture halls and hospital rotations are being complemented — and sometimes transformed — by digital technologies, advanced simulations, and artificial intelligence (AI). These innovations are reshaping how future doctors are trained, making learning more interactive, personalized, and globally accessible.
1. Digital Learning and Online Platforms
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of online learning, and the trend continues:
- E-learning platforms allow students to access lectures, case studies, and interactive modules anytime, anywhere.
- Virtual classrooms enable collaboration across countries, fostering international learning experiences.
- Microlearning and modular courses let students learn in short, focused segments, improving retention.
Digital learning tools also support self-paced study, making medical education more flexible for students balancing clinical rotations.

2. Simulation-Based Learning
Simulations have become a cornerstone of modern medical education:
- High-fidelity mannequins replicate real patient conditions, allowing students to practice procedures safely.
- Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) enable immersive surgical training and anatomy exploration.
- Scenario-based simulations help develop clinical reasoning, teamwork, and decision-making skills without putting patients at risk.
These tools not only enhance technical skills but also reduce errors in real clinical settings.
3. Remote Labs and Virtual Anatomy
Advances in technology are enabling hands-on learning even when students cannot access physical labs:
- Virtual dissection tables and 3D anatomy software allow detailed exploration of human anatomy.
- Remote lab experiments provide real-time data analysis and lab techniques through online platforms.
- Interactive quizzes and simulations enhance understanding of complex biological processes.
These innovations make education more inclusive, allowing students in remote regions to access high-quality resources.
4. Integration of Artificial Intelligence
AI is no longer just a research tool — it’s becoming a teaching assistant:
- AI-driven adaptive learning personalizes study materials based on student performance.
- Predictive analytics help educators identify students who may need extra support.
- Clinical decision simulations allow students to practice diagnosis and treatment planning in a virtual environment.
AI also prepares students for future medical practice, where AI-assisted diagnostics and patient management are increasingly common.

5. Emphasis on Interdisciplinary and Global Skills
European medical schools are increasingly promoting:
- Interprofessional education: Students learn alongside nurses, pharmacists, and other health professionals.
- Global health perspectives: Online collaborations and international electives expose students to diverse healthcare systems.
- Soft skills development: Communication, ethics, and patient-centered care are integrated into the curriculum alongside technical skills.
6. The Future of Medical Education in Europe
The combination of digital tools, simulations, and AI is transforming medical training into a more flexible, personalized, and practice-ready experience. Students who embrace these trends not only gain technical knowledge but also develop the adaptability required in a rapidly changing healthcare environment.
European medical education is moving toward a future where learning is continuous, technology-enhanced, and globally connected — preparing doctors not just for today’s healthcare challenges, but for tomorrow’s innovations.
Final Thoughts
The integration of technology into medical education is no longer optional — it’s essential. Digital platforms, simulation, remote labs, and AI are not just trends; they are shaping the very way medicine is taught and practiced. Students who engage with these tools gain a competitive edge, mastering both clinical skills and technological literacy, crucial for modern healthcare.